At the Mobile World Congress (MWC 2025) held in Barcelona, the GSMA officially released the next-generation SGP.32 eSIM standard, drawing widespread attention across the global IoT industry. Designed for massive IoT devices—including smart sensors, industrial terminals, wearables, and automotive systems—this standard addresses global connectivity, remote provisioning, and security management, removing the physical limitations of traditional SIM cards and offering greater flexibility and deployment efficiency for manufacturers, operators, and enterprise users.
Since the introduction of eSIM (embedded SIM), the IoT sector has aimed to overcome the challenges of SIM swapping, carrier lock-in, and complex configurations. Earlier eSIM standards like SGP.02 and SGP.22 primarily served smartphones and premium devices, but they fell short in meeting the fragmented, automated, and large-scale management needs of the IoT space.
SGP.32 directly addresses these pain points, simplifying global connectivity and lifecycle management for IoT terminals and injecting new energy into smart cities, industrial IoT, connected vehicles, and smart metering scenarios.
SGP.32 eSIM Overview: Key Innovations in IoT Connectivity
SGP.32 is GSMA’s newly tailored eSIM standard for IoT devices and is seen as a “powerful enabler for large-scale remote IoT connectivity.” Compared with previous solutions, SGP.32 focuses on:
- Mass automated deployment: Supports batch activation and remote provisioning for thousands of devices, drastically reducing manual labor and operational costs.
- Flexible carrier switching: Devices can switch carriers remotely based on location or lifecycle, supporting global out-of-box usage and cross-border operations.
- Simplified remote configuration: Offers a standardized remote process, with fast provisioning via OTA (Over-the-Air) updates.
- End-to-end security: Integrates robust identity authentication, encryption algorithms, and lifecycle controls to enhance security and compliance.
--- title: "SGP.32 eSIM Application Architecture in IoT Device Lifecycle" --- graph TD; A["IoT Device (SGP.32 eSIM)"] --> B["Local Activation/Factory Binding"] B --> C["Remote Provisioning Platform"] C --> D["Global Cellular Network (Multi-Carrier)"] D --> E["Remote Lifecycle Management"] E --> F["Security Policy Delivery & Data Encryption"] F --> G["Enterprise Cloud Platform & Services"]
Industry Impact of SGP.32: Global IoT Deployment
SGP.32 is not just a technical upgrade—it’s a key driver of globalization and scalability in the IoT ecosystem. It brings:
- Faster time-to-market: eSIMs can be embedded and pre-activated at the factory. Devices can be used immediately upon delivery—no SIM cards or setup needed.
- Unified global platform management: Enables global connectivity and centralized remote configuration, simplifying international project rollouts.
- Improved security and operations: Devices can receive OTA updates for configuration and security throughout their lifecycle, lowering the risk of hijacking and cloning.
From SGP.02 to SGP.32: Evolution of eSIM for IoT
Earlier eSIM standards by GSMA include SGP.02 (for consumer devices) and SGP.22 (for M2M IoT), each with limitations. SGP.02 suits phones and tablets, while SGP.22 focuses on secure remote management but lacks user-friendliness for bulk operations.
SGP.32 fills the gap by offering lightweight remote provisioning and global unified management for massive-scale IoT deployments.
| Comparison | SGP.02 (Consumer) | SGP.22 (M2M IoT) | SGP.32 (IoT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Use | Phones, laptops, wearables | Automotive, industrial, metering | Sensors, edge devices |
| Provisioning | User self-service | Remote by admins | Bulk automated setup |
| Deployment | Difficult | Complex | One-click OTA provisioning |
| Carrier Switch | Manual | Platform-based | Rule-based, automated |
| Security | High | Higher | End-to-end encryption & auth |
| Ecosystem | Consumer-centric | Industrial/operator | Full IoT ecosystem support |
SGP.32 Architecture: Remote SIM Provisioning and Lifecycle
SGP.32 combines eUICC (embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card) with remote provisioning services (SM-DP+), lowering the barrier for large-scale deployments.
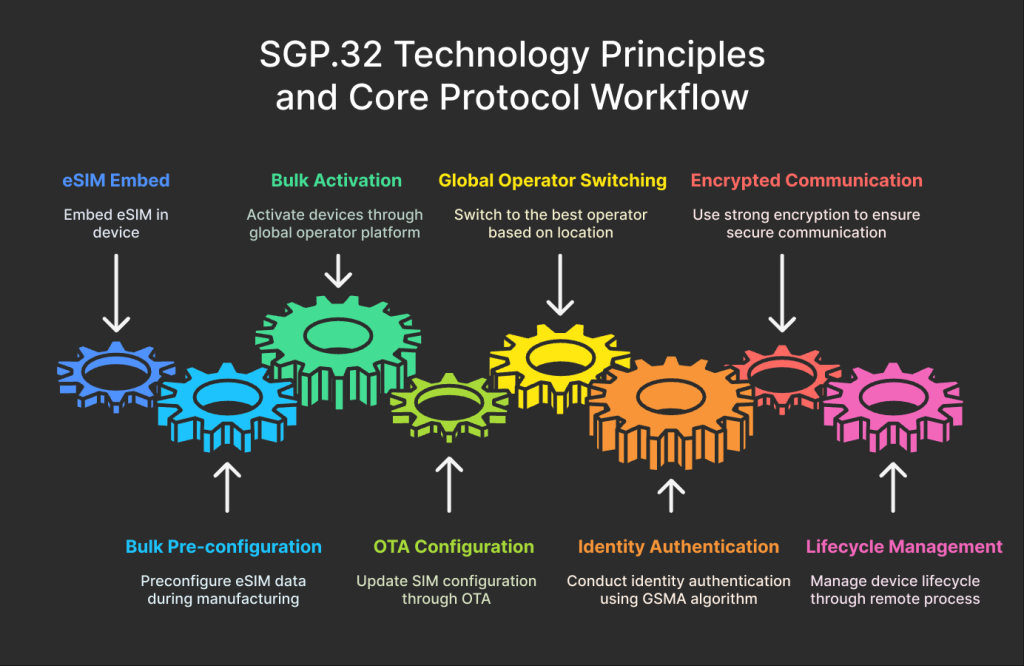
1. Standardized Provisioning and Activation
- Preconfigured in bulk: eSIM credentials can be injected during manufacturing; post-deployment activation happens automatically via global carrier platforms.
- OTA configuration: No physical intervention is needed for carrier switching or updates—everything is pushed remotely.
2. Global Dynamic Carrier Switching
SGP.32 allows devices to choose and switch to the best local carrier based on deployment location.
- Ideal for cross-border logistics, connected vehicles, and wearables.
- Carrier platforms can assign eSIM profiles dynamically based on policies, geofencing, or lifecycle stages.
3. End-to-End Security and Lifecycle Control
- Authentication and encrypted communication: Certified algorithms ensure tamper-proof identities and protect against hijacking.
- Lifecycle management: Devices can be activated, deactivated, or reassigned securely at any stage, ensuring compliance.
Real-World Use Cases: How SGP.32 Enables Secure IoT
Smart Cities & Public Infrastructure
Streetlights, traffic sensors, and environmental monitors can be configured in bulk, enabling plug-and-play deployment and remote updates to cut costs.
Connected Vehicles & Logistics
Smart containers and fleet vehicles can automatically switch networks across borders, with remote controls to freeze or restore connectivity in emergencies.
Industrial IoT & Smart Metering
Smart meters for water, electricity, or gas can be embedded with eSIMs at the factory. Once deployed, they connect automatically and securely for remote monitoring.
mermaid
--- title: "SGP.32 Remote Provisioning Flow in Connected Vehicles" --- flowchart TD A["Vehicle Preloaded with SGP.32 eSIM"] --> B["Global Carrier Registration"] B --> C["Auto-activation on Road"] C --> D{"Cross-border?"} D -- "No" --> E["Connect to Local Network"] D -- "Yes" --> F["Auto-switch to Optimal Carrier"] E & F --> G["Data Securely Uploaded to Cloud"] G --> H["Remote Operations & Updates"]
SGP.32 Deployment Best Practices for Scalable IoT
SGP.32 enables plug-and-play experiences with bulk remote provisioning and secure management. Recommendations include:
1. Factory Integration & Activation
- Embed and register eSIMs during manufacturing.
- Use production-line activation to sync device IDs with platforms.
2. Platform Integration & Automation
- Connect to certified provisioning platforms (SM-DP+/SM-DS) for centralized management.
- Enable custom rules for batch configurations across projects.
3. Remote Security and Lifecycle Management
- Push regular updates and security policies remotely to prevent threats.
- Define activation, sleep, deactivation, and retirement processes.
4. Seamless Integration with IoT/IT Systems
- SGP.32 can interface with enterprise IoT platforms, ticketing systems, and analytics engines.
- Use APIs to automate provisioning and anomaly handling.
Global Trends in eSIM and Secure IoT Management
SGP.32 will accelerate global deployment, remote operations, and international business in IoT.
Future directions include:
- Full automation: From manufacturing to retirement—all managed remotely and automatically.
- Multi-carrier switching: Auto-switch based on geography, signal quality, or compliance.
- Stronger security: Continued upgrades in identity, encryption, and lifecycle safety.
- Expanding ecosystem: Collaboration among operators, OEMs, and platform providers.
- Integration with AI & Blockchain: Enabling intelligent and trustworthy IoT infrastructure.
Use Cases
Smart City Terminal Deployment
A European smart city project used SGP.32 to manage tens of thousands of sensors and lights. eSIMs were preloaded at the factory. No SIM cards or manual steps needed onsite. Carrier switching took just one click, cutting O&M costs dramatically.
Global Logistics & Fleet Operations
A global logistics provider equipped cargo units and vehicles with SGP.32 eSIMs. Devices auto-switched networks across borders. In case of theft or issues, connectivity could be frozen or rerouted remotely, securing valuable assets end-to-end.
SGP.32: A New Era of Secure, Scalable IoT Connectivity
SGP.32 sets a new standard for secure, efficient, and scalable IoT device connectivity. It boosts operational efficiency, safety, and business agility in smart manufacturing, smart cities, automotive, metering, and more.
With continued growth in technology and ecosystems, SGP.32 is poised to drive the next wave of globally connected, remotely managed, and securely operated IoT infrastructure.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about SGP.32
Q1: What is SGP.32 and how is it different from previous eSIM standards?
A1: SGP.32 is a GSMA standard designed for massive IoT deployments. Unlike SGP.02 and SGP.22, it supports remote sim provisioning, secure management, and automated global carrier switching.
Q2: Can SGP.32 improve IoT connectivity for global deployments?
A2: Yes. SGP.32 enables flexible, secure, and carrier-independent connectivity across regions, making it ideal for logistics, smart cities, and industrial IoT applications.
Q3: How does SGP.32 enhance secure device management?
A3: Through end-to-end encryption, secure provisioning, and OTA updates, SGP.32 ensures the integrity and security of IoT device identities across their lifecycle.
Q4: What types of IoT devices benefit most from SGP.32?
A4: Smart meters, logistics trackers, vehicles, wearables, and industrial edge devices that require remote provisioning and multi-region support.


