This article looks at practical patterns for tuya ai integration without modifying device firmware or cloud architecture.
Modern IoT deployments generate far more data, conditions, and edge cases than static rule‑based logic can handle. Tuya provides a reliable foundation—device connectivity, DP models, cloud routing, and mobile SDKs—while AI brings the reasoning layer needed to interpret this data and decide what should happen next. This combination enables systems that react to context rather than predefined scripts.
1. Why AI Matters for Tuya-Based IoT Systems
Tuya’s platform is excellent at consistent tasks: onboarding devices, reporting DP values, and providing stable cloud and LAN control channels. What it doesn’t attempt to solve is higher‑order decision logic. AI complements Tuya by turning raw sensor data into meaningful insights and actions, without modifying device firmware or Tuya protocols.
This combination has become the most common pattern for practical Tuya AI integration, especially in data-driven environments.
2. Verified Tuya Capabilities
Before implementing AI logic, it’s essential to understand the official capabilities that Tuya exposes through its API and SDK ecosystem. These official APIs form the foundation required for any practical tuya ai integration workflow.
2.1 Tuya Cloud API
Docs: https://developer.tuya.com/en/docs/cloud/overview
The Cloud API is the core interface for server‑side automation. It supports:
- Querying device state
- Controlling devices
- Receiving DP events through webhooks
Example command:
POST /v1.0/devices/{id}/commands
{
"commands":[{"code":"switch","value":true}]
}For most backend systems, a Tuya Cloud API AI architecture offers the cleanest path to server-side automation.
Service reference:
Tuya Cloud development services
2.2 Tuya App SDK (iOS / Android)
Docs: https://developer.tuya.com/en/docs/app-development/overview
The App SDK is suitable for interactive or UI‑driven use cases. It supports:
- Real‑time DP streams
- Local and cloud control
- Custom React Native / native UI panels
- User and room structures
Interactive scenarios, such as contextual guidance and natural-language explanations, typically rely on Tuya SDK AI patterns.
Migration details:
OEM to SDK Migration Guide
2.3 Tuya Device SDK / TuyaOS
Docs: https://developer.tuya.com/en/docs/iot/device-sdk-overview
TuyaOS is used for embedded logic, DP parsing, and OTA updates. Tuya’s documentation clarifies that on‑device AI agents are not supported yet, so AI logic should stay in the cloud or app layer.
3. What AI Can and Cannot Do
AI does not bypass Tuya or replace device firmware. Instead, its role is to work alongside Tuya’s existing DP model and cloud/device APIs to perform tasks that static rules alone cannot cover. In a typical system, AI is responsible for understanding context, identifying patterns, and deciding when something is meaningful enough to trigger an action.
AI is useful for:
- Interpreting DP values beyond thresholds
(e.g., understanding whether a temperature spike is normal based on historical patterns) - Evaluating multi-sensor conditions
(motion, temperature, occupancy, light levels, timing—combined logically) - Generating suggested actions
(e.g., “turn on AC”, “send alert”, “wait for more data”, “ignore false triggers”) - Triggering device commands through Tuya Cloud API or App SDK
(AI never directly touches device hardware; Tuya remains the execution layer)
What AI cannot do:
- It cannot modify or override Tuya firmware
- It cannot change DP definitions or device capabilities
- It cannot run inside most Tuya devices (no on-device LLM support)
- It cannot bypass Tuya’s cloud routing or pairing process
This clear division of responsibilities keeps systems stable, safe, and maintainable during long-term operation.
4. How AI-Driven Workflows Operate with Tuya
RRegardless of the model or cloud environment, most AI-driven automations follow a predictable flow.
The goal is to keep AI responsible for reasoning, while Tuya remains responsible for device execution and reliability.
- Collect device data via Tuya Cloud API or SDK
DP reports, device status queries, event callbacks, or user-triggered actions provide the raw context AI needs. - Send structured payloads to an AI model
The AI receives a clean, normalized JSON structure—usually a subset of relevant DP values and recent history. - AI analyzes context or predicts conditions
The model can detect anomalies, interpret multi-sensor relationships, understand user intent, or reason over patterns. - AI outputs a decision or recommended action
This might be a device command (“turn on”), a delay (“wait 5 minutes”), a user-facing explanation, or a risk evaluation. - Tuya executes commands through Cloud API or SDK
All actions must be sent back to Tuya in the form of officially supported commands.
Tuya remains the source of truth for device control. - Optional: automate the loop using n8n or backend cron
Event-driven pipelines can run continuously without manual intervention.
This pattern allows AI to evolve or improve without touching device firmware, while relying on Tuya for safe, predictable hardware-level behavior.
5. Proven Architectures for AI + Tuya
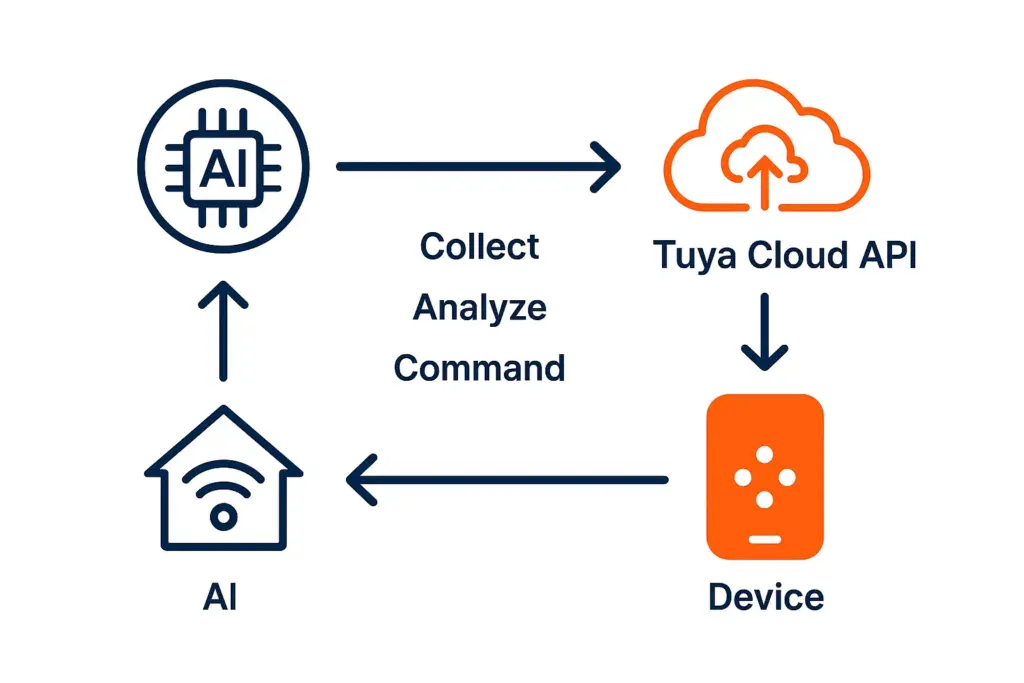
These approaches represent common structures in AI IoT automation, balancing device reliability with cloud-based intelligence.
Architecture 1: AI + Tuya Cloud API
This server‑side approach is the most robust for enterprise systems.
Device → Tuya Cloud → Webhook → AI Service → Tuya Cloud API → DeviceExample DP event:
{
"device_id": "abc123",
"status":[{"code":"temp","value":31.2}]
}Automation example:
AI automation workflows with n8n
Architecture 2: AI + Tuya App SDK
Used when AI needs to inform UI or assist users directly.
App SDK → AI Model → App SDK → Device ControlTypical use cases include natural‑language device explanations and adaptive UI flows.
Architecture 3: AI + n8n (Event Automation)
n8n can orchestrate the entire AI → Tuya → AI loop without building custom servers.
Tuya Event → n8n → AI → n8n → Tuya Cloud API6. Tuya’s AI Agent Development Platform
Docs: https://developer.tuya.com/en/docs/iot/ai-agent-management
Tuya provides a cloud‑based AI Agent framework that integrates LLMs, device‑control plugins, and panel/cloud deployment. However, per official documentation, device‑side deployment is not supported: https://developer.tuya.com/en/docs/iot/AI-feature
This means AI logic should remain in cloud or app layers for now.
7. Real-World Use Cases
Together, these patterns form the foundation of scalable tuya ai workflows across consumer and industrial applications. In real deployments, the value of AI usually comes from interpreting device data more intelligently—not from adding new device-side capabilities. Below are examples we’ve implemented or validated in projects using only Tuya’s Cloud API, App SDK, and DP reporting models.
- Smart energy optimization
AI identifies patterns in energy usage (temperature, occupancy, load cycles) and pushes commands through Tuya Cloud API to reduce unnecessary consumption. - HVAC and environmental control
Multi-sensor inputs—temperature, humidity, CO₂ levels, window states—are combined by AI to produce more stable HVAC adjustments than static rules. - Multi-sensor reasoning
Instead of treating each DP event independently, AI correlates motion, light levels, and time-of-day to decide whether a trigger is meaningful. - Predictive maintenance triggers
AI evaluates historical DP trends (e.g., compressor cycles, temperature drift, motor current) to flag early signs of equipment issues. - Natural-language summaries for end users
AI converts raw DP values into easy-to-read messages such as
“Your device has been running heavier than usual today.”
improving app UX without modifying device firmware.
All of these scenarios rely strictly on existing Tuya SDK and Cloud API capabilities—no custom firmware, local models, or unsupported device behavior. In practice, these scenarios are where tuya ai integration starts to show measurable value.
8. Recommended Production Architecture
The most reliable pattern we see across deployments:
Tuya Cloud API → AI Service → Decision Layer → Tuya CommandIt avoids hardware constraints and scales well to multi‑device environments.
9. OEM, SDK, or Cloud?
Choosing the right entry point impacts how much control AI can have.
| Option | AI Suitability | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| OEM App | Very low | No custom logic |
| MiniApp | Limited | Restricted environment |
| App SDK | High | Best for UI + AI |
| Cloud API | High | Best for automation |
| n8n | High | Ideal for orchestration |
For deeper customization:
OEM → SDK migration
10. How ZedIoT Helps
We design and implement AI‑powered workflows using official Tuya components. Our work includes:
- Tuya App SDK development
- Cloud API automation pipelines
- n8n orchestration
- AI decision engine integration
- DP modeling
- Multi‑cloud infrastructure
Learn more:
Full‑stack Tuya development services
Need support with AI‑driven Tuya architectures or custom workflows? Our engineering team helps design practical, maintainable solutions tailored to your device ecosystem.
→ Discuss Your Technical Requirements
FAQ
Does Tuya support on‑device AI?
Not currently. AI must run in the cloud or app layer.
How does AI control devices?
AI outputs decisions; Tuya Cloud API or App SDK performs the control.
Does Tuya provide real‑time events?
Yes, via webhooks for DP updates.
Which architecture is recommended?
AI + Tuya Cloud API with server‑side orchestration.

