Employee tracking is becoming increasingly important in smart retail as companies look beyond devices—such as energy-saving freezers, digital signage, and AI foot-traffic analytics—to truly enhance their operations.
However, in day-to-day store activity, the factor that most directly shapes the customer experience is still the quality and consistency of employee service.
Even the most advanced retail technologies cannot compensate for poor interactions. A single negative checkout experience or inconsistent service moment can weaken customer trust and affect brand perception. For large chains, the behaviors of thousands of employees collectively define retail service quality and customer retention.
This is why modern retailers are adopting AI-powered employee tracking—not to “monitor people,” but to establish measurable, consistent, and real-time service standards across stores. Smart AI employee monitoring offers a scalable way to ensure compliance, strengthen staff safety, reduce errors, and maintain operational consistency without relying solely on manual supervision.
Challenges in Traditional Staff Management
Traditional store management relies heavily on manual supervision and subjective judgment:
1. Difficult to supervise
Managers cannot observe every service interaction throughout the day, especially in large stores.
2. No objective evaluation
Performance is often measured through customer complaints or occasional audits—samples far too limited to represent true behavior.
3. Safety and compliance risks
Improper checkout operations, mishandling items, or ignoring procedures create financial and safety risks.
4. Unclear training effectiveness
Even with centralized training, stores lack a mechanism to confirm whether employees follow new standards.
As operations scale, chains need systems that support real-time tracking of retail store compliance, rather than relying on inconsistent manual checks.
AI-Driven Smart Staff Management in Retail Service Quality
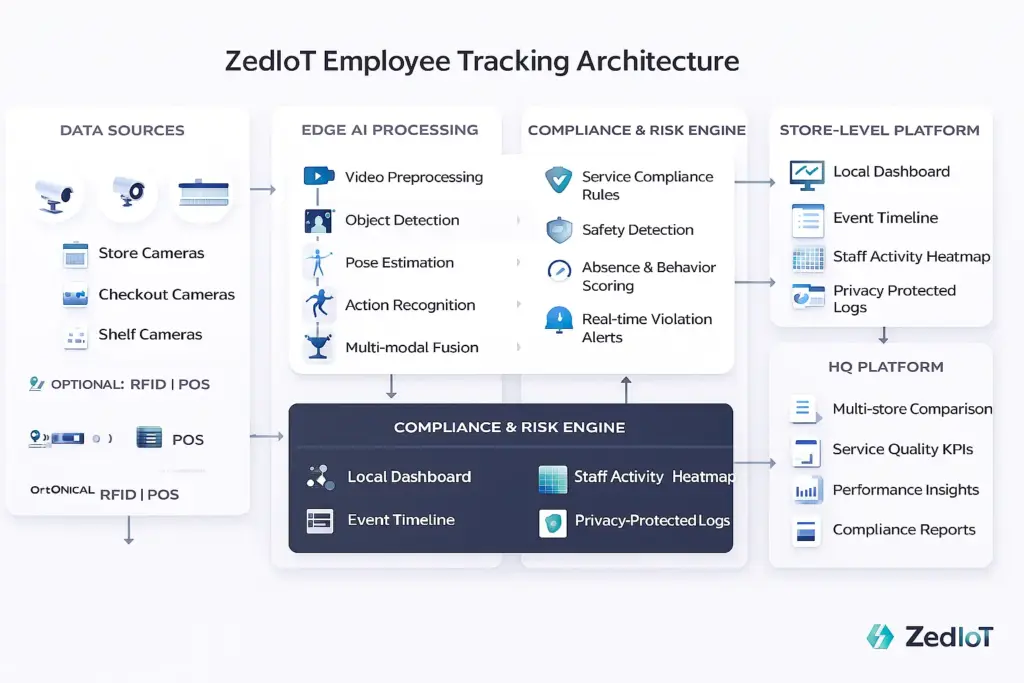
Modern retailers are adopting employee behavior monitoring software with real-time analytics to automate behavior recognition and compliance tracking.
The system uses:
- Computer vision to detect service actions, stocking, checkout behavior, and posture
- AI behavior analysis to classify whether actions follow standard workflows
- Real-time alerts to notify managers of potential risks
- Data logging to support employee coaching, KPI measurement, and operational audits
This provides transparency, measurable service standards, and higher operational reliability.
How AI Behavior Recognition Works
AI staff behavior monitoring typically combines computer vision + edge AI inference.
Flow as follows:
--- title: "Store Employee Behavior Recognition Workflow" --- graph TD A["🎥 Video Stream from Cameras"] B["🤖 Edge AI Inference Device"] C1["🆔 Staff Identity Detection<br/>(Badge / Uniform)"] C2["📊 Action Recognition<br/>(Stocking / Checkout / Service)"] C3["⚠️ Violation Detection<br/>(Absence / Irregular Checkout)"] D["📝 Behavior Data Logging"] E["🚨 Real-time Alerts"] F["📈 Staff Performance Evaluation System"] G["🖥️ Manager / HQ Dashboard"] A --> B B --> C1 B --> C2 B --> C3 C1 --> D C2 --> D C3 --> E D --> F E --> G
Key points:
- Most AI inference runs locally on edge devices, reducing delay.
- Only essential results are uploaded to HQ for consolidated reporting.
Initial Value Delivered
Deploying an AI-driven staff monitoring system brings immediate benefits:
1. Operational efficiency
- Managers no longer need to rely on manual inspections.
- Automated behavioral reports provide full visibility.
2. Risk reduction
- The system detects irregular or unauthorized behavior in real time.
3. Service standardization
- Training standards can finally be turned into measurable, enforceable behaviors.
4. Better training outcomes
- Historical data highlights weak areas, enabling targeted coaching.
The Technical Foundations Behind AI Employee Behavior Monitoring
Employee behavior monitoring in smart retail essentially integrates AI computer vision, sensor data collection, and edge computing into a unified system. To achieve measurable, real-time, and traceable supervision, each technical component must be carefully designed.
1. Computer Vision & Action Detection
The core technologies include computer vision (CV) and deep learning models.
• Object Detection
Used to identify employee-related features such as uniforms or name badges.
Common models include YOLO and Faster R-CNN.
• Pose Estimation
Detects body keypoints to determine whether staff are performing normal service actions—stocking, checkout, assisting customers—or performing improper actions (e.g., looking down at a phone for long periods).
Typical models: OpenPose, HRNet.
• Action Recognition
Analyzes sequences of video frames to classify behaviors.
For example, distinguishing between “restocking” and “mishandling products.”
Common methods: 3D CNNs or Transformer-based video recognition.
2. Multi-Modal Data Fusion
Vision data is enhanced with additional signals:
- RFID / barcode scans to verify stocking and checkout consistency
- Indoor positioning to detect prolonged absence from assigned areas
- Voice data to evaluate service interactions when appropriate
This fusion reduces false positives and increases accuracy in AI behavior recognition.
3. Edge Computing for Real-Time Performance
Uploading full video to the cloud is inefficient and raises privacy concerns.
Instead, most systems use edge devices (Jetson, RK3588, Coral TPU):
- AI inference runs locally
- Only compressed results or events are uploaded
- Supports real-time tracking of retail store compliance
- Reduces latency and bandwidth usage
This architecture is essential for large retail environments with many cameras.
4. Rule Engine and Compliance Logic
Raw AI outputs are processed by a rule engine to determine:
- Standard actions vs. abnormal events
- Thresholds for alerts (e.g., absence > 10 minutes)
- Compliance scoring for coaching and training
- Cross-store operational comparisons
This transforms the system into a store staff operation compliance monitoring system, tailored to retail procedures and safety standards.
--- title: "AI Employee Behavior Monitoring Logic" --- graph TD A["🎥 Camera / Sensor Data"] B["🤖 AI Recognition Model"] C["📊 Behavior Results"] D["⚙️ Rule Engine"] E1["✅ Normal Behavior Logged"] E2["🚨 Abnormal Behavior Alert"] F["🗄️ Behavior Database"] G["🖥️ Manager / HQ Notification"] A --> B B --> C C --> D D --> E1 D --> E2 E1 --> F E2 --> G
5. Data Protection and Privacy
Modern deployments rely on:
- Local storage for raw video
- Anonymized uploads for central analytics
- Audit mechanisms for compliance with GDPR and national cybersecurity laws
- Clear employee policies to ensure transparency and acceptance
This ensures responsible use while enabling operational improvements.
6. System Integration and Scalability
Employee behavior monitoring integrates with:
- ERP and attendance systems
- Training and LMS platforms
- Safety systems
- Task management tools
This creates a complete operational loop—not a standalone surveillance tool.
These capabilities can also be extended through our broader AIoT platform, which integrates device data, edge intelligence, and multi-store management into one system.
Functional Module Breakdown
| Module | Technology | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Vision Recognition | YOLO, Pose Estimation | Identify staff & behavior |
| Action Analysis | 3D CNN, Transformers | Classify service vs. abnormal actions |
| Multi-Modal Fusion | RFID, audio, positioning | Reduce false positives |
| Edge Computing | Jetson / TPU | Real-time inference |
| Rule Engine | Compliance logic | Alerts, scoring |
| Data Privacy | Local storage, anonymization | Regulatory compliance |
| Integration | ERP / training / safety | Operational loop |
Industry Concerns and Real Value
Key Concerns from Retailers and Operators
Employee behavior monitoring is not just an AI tool—it directly affects operations, management, and brand reputation. When retailers consider implementing such systems, they typically focus on several critical questions.
1. Cost & ROI
Retailers care deeply about overall investment, including:
- Hardware: cameras, edge devices, storage, network upgrades
- Software/platform fees: AI model licensing, SaaS subscription, or private deployment
- Maintenance: algorithm updates, device replacement, technical support
Common questions include:
Scalability: Can the system scale across hundreds of stores without rework?
ROI cycle: Most deployments recover costs within 12–18 months.
Hidden savings: Reduced manual inspections, fewer losses from improper operations.
2. False Alarms & Accuracy
Too many false positives lead to distrust from both staff and managers.
Retailers want to know:
- Whether the detection accuracy is ≥ 95%, especially for checkout and service actions
- How multi-modal data can reduce false alarms
- Whether thresholds can be adjusted to match different store workflows
3. Employee acceptance
Employees are the frontline users. If the system creates stress, it may backfire.
Industry best practices include:
- Positive incentives: Tie AI behavior scores to awards instead of only penalties
- Transparent communication: Explain what behaviors are monitored to avoid fear
- Training integration: Use data to help employees improve—not simply “monitor” them
4. Operational usefulness
Retailers care less about “detecting violations” and more about whether data can be used to improve operations:
- Employee productivity tracking and monitoring
- Service quality improvement
- Risk reduction
- Cross-store performance comparisons: Use behavior logs to trace safety issues or financial discrepancies
5. Regulation & Staff Safety Compliance
Data privacy and employee rights are increasingly regulated worldwide.
Retailers must consider:
- Does the system support local storage + anonymized uploads?
- Are employee data review and appeal mechanisms available?
- Does the system comply with GDPR, national cybersecurity laws, and internal policies?
These factors often determine whether the system can scale across a chain.
Industry Perspective: Real Value Delivered
Based on retailer feedback and industry practice, the system’s core value can be summarized:
| Focus Point | What Retailers Expect | Actual Value Delivered |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Control | ROI ≤ 18 months | Reduced labor cost + lower loss from violations |
| Accuracy | ≥95% detection | Multi-modal fusion reduces false alarms |
| Employee Experience | Low resistance | Incentives + transparency improve acceptance |
| Management Use | Measurable KPIs | Standardized metrics for cross-store comparison |
| Compliance | Legal and safe | Local storage + anonymization meet regulations |

Final thoughts about Employee Tracking in Retail
Retailers care less about flashy AI terms and more about practical adoption:
- How much to invest, and how fast can it pay back?
- Can it integrate smoothly with existing store management systems?
- Can the data help improve training and service, not just monitor staff?
- Can compliance and employee acceptance be achieved at the same time?
By combining employee tracking, AI-based action recognition, and real-time operational analytics, retailers can achieve measurable improvements in service quality, safety, and operational consistency across stores.
“If you’re exploring ways to enhance service consistency, safety, and daily operations across your stores,
our retail store management software provides a fully integrated AI + IoT workflow designed for real-world
retail environments.Contact us to discuss your project.

